Project Info
Category
Date
AI-Generated “Snow Apocalypse” Footage Falsely Linked to Kamchatka’s Record Snowfall
The Viral Claim and the Moment It Emerged
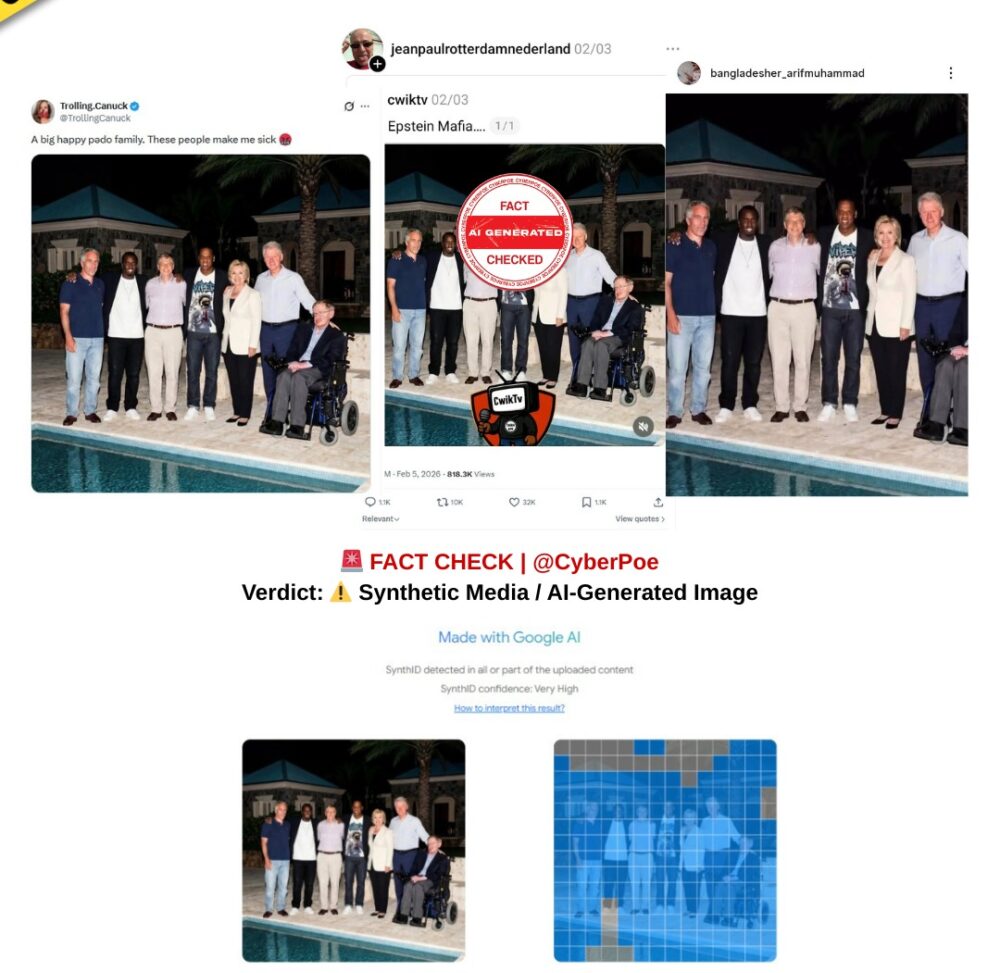
In January 2026, Russia’s far-eastern Kamchatka Peninsula experienced one of its most severe snowfalls in decades.[1] The scale of the storm was real and disruptive. Authorities declared a state of emergency, public institutions closed, and emergency crews worked continuously to clear roads, dig out homes, and prevent further casualties after snow collapsing from rooftops killed at least two people. Against this authentic backdrop of crisis, a series of highly dramatic videos began circulating across social media platforms, including Facebook,[2] TikTok,[3] X,[4] and Threads.[5] These clips showed vast, perfectly formed snowdrifts rising several storeys high and swallowing entire apartment buildings, presented as evidence that Kamchatka had descended into an almost apocalyptic winter catastrophe.
The videos were widely described as proof of a “snow apocalypse,” with captions asserting that the region had been buried beyond recognition. Because the claim coincided with legitimate news coverage confirming unusually intense snowfall, many viewers accepted the footage at face value. The emotional power of the visuals, combined with real reports of disruption and fatalities, created an environment in which skepticism was muted and sharing accelerated rapidly across languages and borders.
The Reality on the Ground in Kamchatka
There is no dispute that Kamchatka faced extreme winter conditions in early January 2026. Official imagery released by Russia’s Ministry of Emergency Situations and covered by independent media outlets shows snow piled high along streets, vehicles buried up to their windows, and rescuers clearing entrances to residential buildings. These images are striking but grounded in physical reality. Snow accumulates unevenly, collapses under its own weight, and interacts chaotically with wind, terrain, and human structures.
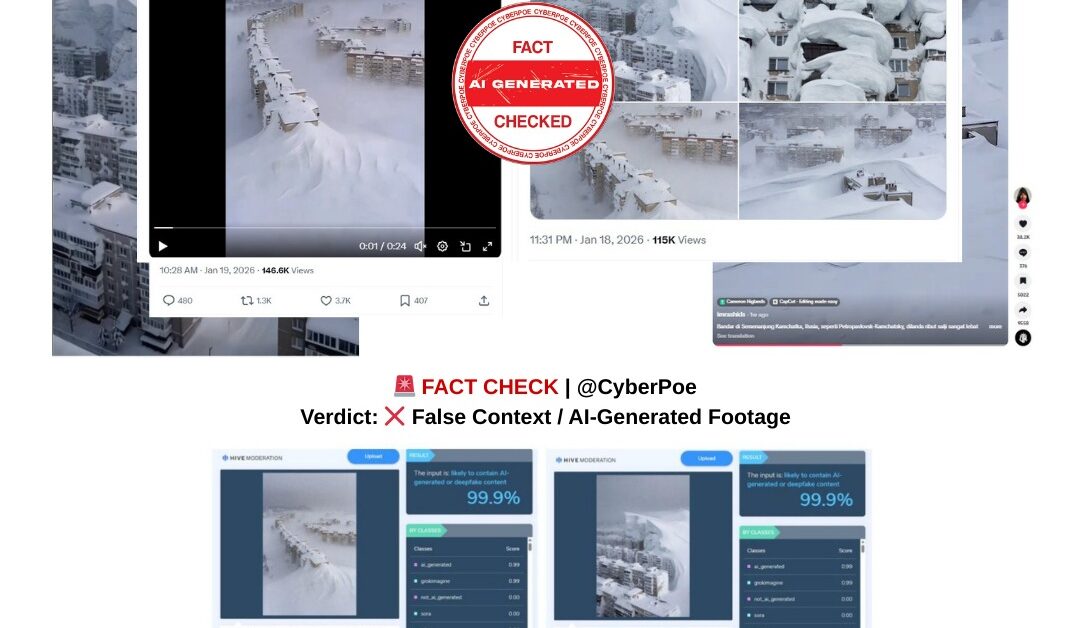
By contrast, the viral clips depict snow formations that appear implausibly smooth and architecturally precise. Entire building facades are shown encased in vertical walls of snow that rise cleanly upward without sagging or collapse. Such formations do not appear in any verified footage from Kamchatka or similar extreme-weather events elsewhere. The disconnect between confirmed documentation and the circulating videos prompted closer examination.
Forensic Review and Signs of Artificial Generation
CyberPoe conducted a detailed visual and technical analysis of the viral footage. Multiple indicators point to artificial generation rather than authentic recording. The snow surfaces in the clips are unnaturally uniform, lacking the irregular textures and break patterns seen in real accumulations. Architectural elements such as windows, balconies, and rooflines subtly distort between frames, as if the underlying structure is being approximated rather than accurately rendered. These inconsistencies are characteristic of generative AI imagery, particularly when static images are animated into video.
Further assessment using Hive Moderation’s[1] AI-detection tools concluded that all of the clips in the viral montage were likely AI-generated or deepfake content. The lighting, depth perception, and motion within the scenes behave in ways inconsistent with real-world physics, reinforcing the conclusion that the footage is synthetic.
Tracing the Origin of the Imagery
Reverse image searches led CyberPoe to earlier still images posted on the platform Threads on January 17, 2026, by a Russian-language account using the handle “ibotoved.”[1] These images were captioned simply as “Kamchatka today,” with no initial disclosure that they were artificial. The viral videos appear to be animated or enhanced versions of these stills, designed to increase their dramatic impact.
As the images spread and users began questioning their authenticity, the account owner later acknowledged that the visuals were created using Grok, an AI assistant developed by xAI. On January 20, the same user published a follow-up post explicitly stating that the images were fake, describing them as a prank and warning viewers not to believe everything they see online.[2] By that point, however, the videos had already traveled far beyond their point of origin, detached from the creator’s admission.
Why the Misinformation Took Hold
This case illustrates how AI-generated visuals can seamlessly blend into real news cycles, particularly during genuine crises. When audiences expect extreme imagery, exaggerated visuals feel plausible rather than suspicious. The absence of clear labeling, combined with rapid cross-platform sharing and language translation, allowed the footage to circulate as supposed documentation long after its artificial origin was established. The Kamchatka snowfall was real and serious, but the most extreme images associated with it were not. By exaggerating reality through synthetic visuals, the misinformation distorted public understanding of the event and demonstrated how easily AI-generated content can hijack authentic news narratives.
CyberPoe Conclusion
The viral videos depicting enormous, multi-storey snowdrifts engulfing apartment buildings in Kamchatka do not represent real footage from the January 2026 snowfall. While the region did experience severe winter conditions, the most dramatic clips circulating online were generated using artificial intelligence and later acknowledged as such by their creator. Presenting these visuals as authentic disaster documentation strips them of context and misleads audiences during a real humanitarian and infrastructural crisis.
CyberPoe | The Anti-Propaganda Frontline 🌍