Project Info
Category
Date
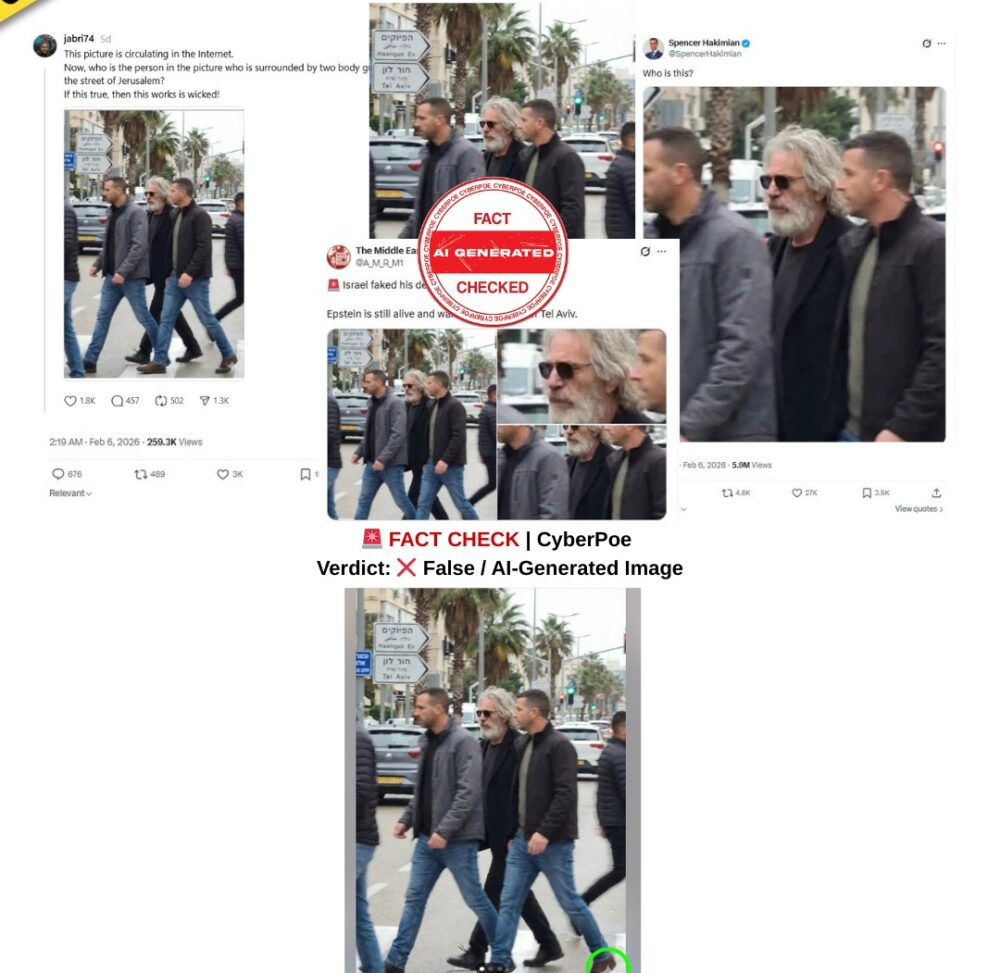
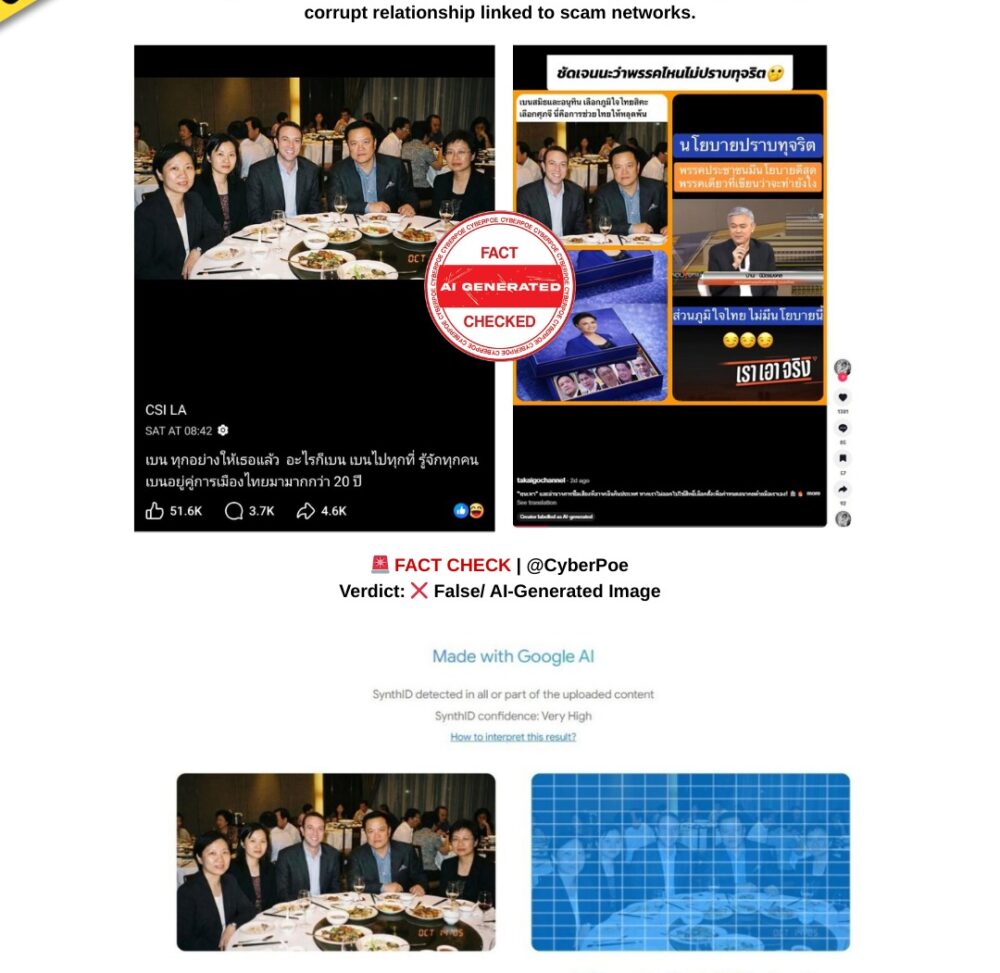
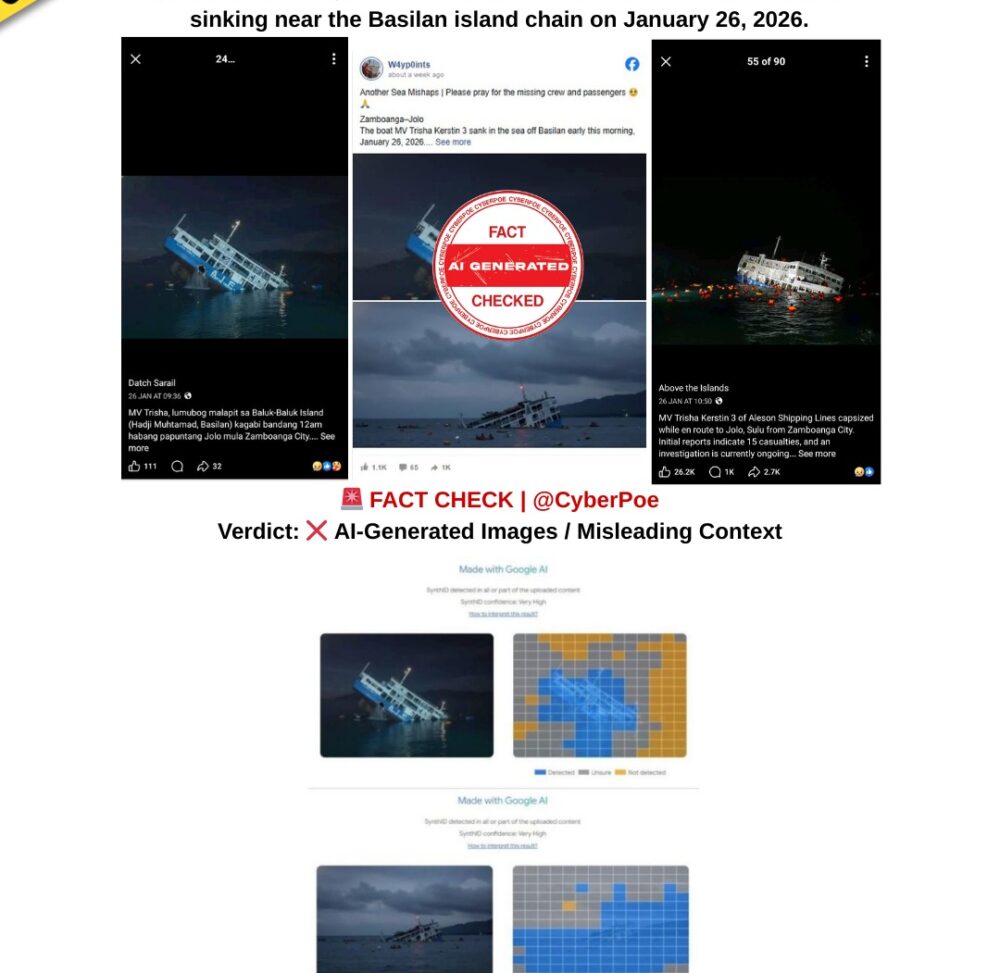
Poolside Image of Jeffrey Epstein With High-Profile Figures Is AI-Generated
The Viral Claim and Its Timing
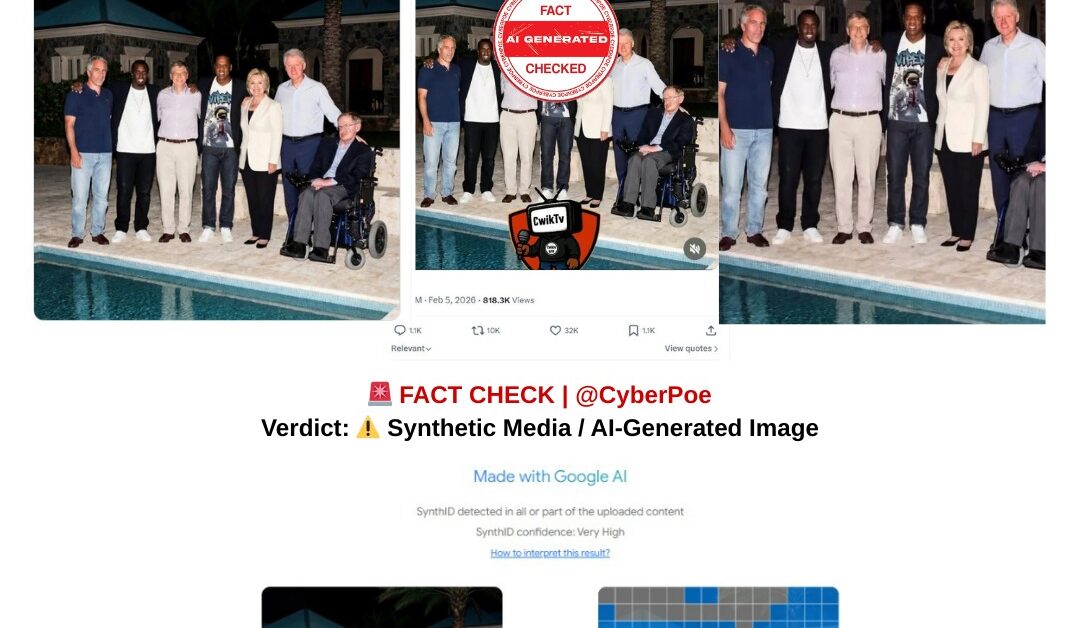
A provocative image circulating widely across social media platforms purports to show Jeffrey Epstein standing beside a swimming pool alongside several globally recognised figures, including Sean “Diddy” Combs, Bill Gates, Jay-Z, Hillary Clinton, Bill Clinton and the late astrophysicist Stephen Hawking. The image is being framed as a 2006 photograph that allegedly captures a private gathering of political, business and entertainment elites connected to Epstein.
The image gained traction amid renewed public scrutiny following the US Department of Justice’s release of a substantial volume of documents related to Epstein’s contacts and communications. In online discussions already shaped by distrust, speculation and political polarisation, the photograph was presented as visual confirmation of an alleged hidden network of influence.
The implication embedded within viral captions is clear: the image is positioned not merely as a photograph, but as evidence. However, technical and contextual verification demonstrates that the image is not authentic.
Technical Analysis and AI Detection
Digital examination using Google’s SynthID detection system indicates that the poolside image contains watermark signatures consistent with artificial intelligence–generated content. [1]SynthID is designed to identify imperceptible markers embedded within images produced by certain AI models. Detection results show patterns aligned with synthetic generation rather than traditional photography.
Beyond watermark detection, structural indicators also raise concerns. The lighting across subjects appears unnaturally uniform despite differing body positions and implied light sources. Depth-of-field transitions do not reflect realistic optical behaviour. Facial alignment and proportional scaling among individuals reveal subtle distortions typical of AI composite rendering. While such anomalies may not be immediately obvious to casual viewers, they are consistent with known characteristics of machine-generated imagery.
Crucially, no verifiable metadata accompanies the image. There is no credited photographer, no historical agency archive, no publication trail and no authenticated record placing all of the depicted individuals together in the configuration shown.
Absence of Archival Corroboration
There is no verified photographic documentation confirming that Epstein was ever photographed in a poolside setting alongside all the named figures simultaneously. While certain individuals have appeared in publicly documented contexts connected to Epstein including meetings, public events or references within archived materials those documented instances do not authenticate this specific visual.
The Department of Justice’s document release includes references to numerous public figures across politics, academia and business.[1] However, the presence of a name in archived files does not establish wrongdoing, nor does it validate the authenticity of viral imagery claiming to depict private gatherings.
Major news agencies and independent fact-checking bodies have not identified any credible archival source for the image. A spokesperson representing Bill Gates publicly confirmed the image is fabricated. No official DOJ channel has authenticated the photograph.
In the absence of corroborating evidence from established media archives or institutional sources, the image remains unsupported by documented history.
Synthetic Media and Narrative Construction
Artificial intelligence tools are increasingly capable of generating highly realistic composite images featuring real public figures. These visuals often surface during moments of heightened public attention, when document releases, court developments or political shifts generate emotional engagement.
The poolside setting depicted in the viral image mirrors recurring tropes associated with Epstein-related conspiracy narratives. By assembling multiple high-profile individuals into a single frame, the image creates visual proximity that implies coordinated association. This technique leverages a powerful psychological effect: viewers tend to interpret photographic co-presence as factual documentation rather than constructed fiction.
Synthetic media of this nature functions as narrative acceleration. It compresses complexity into a single emotionally charged visual, bypassing the nuance required for evidence-based evaluation.
Why Verification Matters
The digital information environment now allows fabricated visuals to circulate at speed, often detached from source attribution or historical verification. AI-generated imagery can combine real individuals into imagined scenarios that exploit existing controversies and public distrust.
In this case, the image’s virality coincided with a legitimate document release, creating a context in which viewers were primed to interpret the fabricated scene as confirmation of suspicions. Without technical verification tools and archival cross-referencing, synthetic content can rapidly be mistaken for historical record.
CyberPoe Verdict
The poolside image showing Jeffrey Epstein with Sean “Diddy” Combs, Bill Gates, Jay-Z, Hillary Clinton, Bill Clinton and Stephen Hawking is AI-generated. Detection analysis identifies synthetic watermark signatures, and there is no credible archival evidence supporting the existence of such a photograph.
The image does not represent authenticated historical documentation. It is a digitally fabricated composite designed to visually associate prominent individuals within a controversial narrative framework.
As artificial intelligence continues to blur the boundary between reality and fabrication, rigorous verification remains essential. Evidence must precede conclusion, and imagery no matter how compelling requires authentication before it can be treated as fact.
CyberPoe | The Anti-Propaganda Frontline 🌍